What causes snoring? What makes the sound? What to do about it?
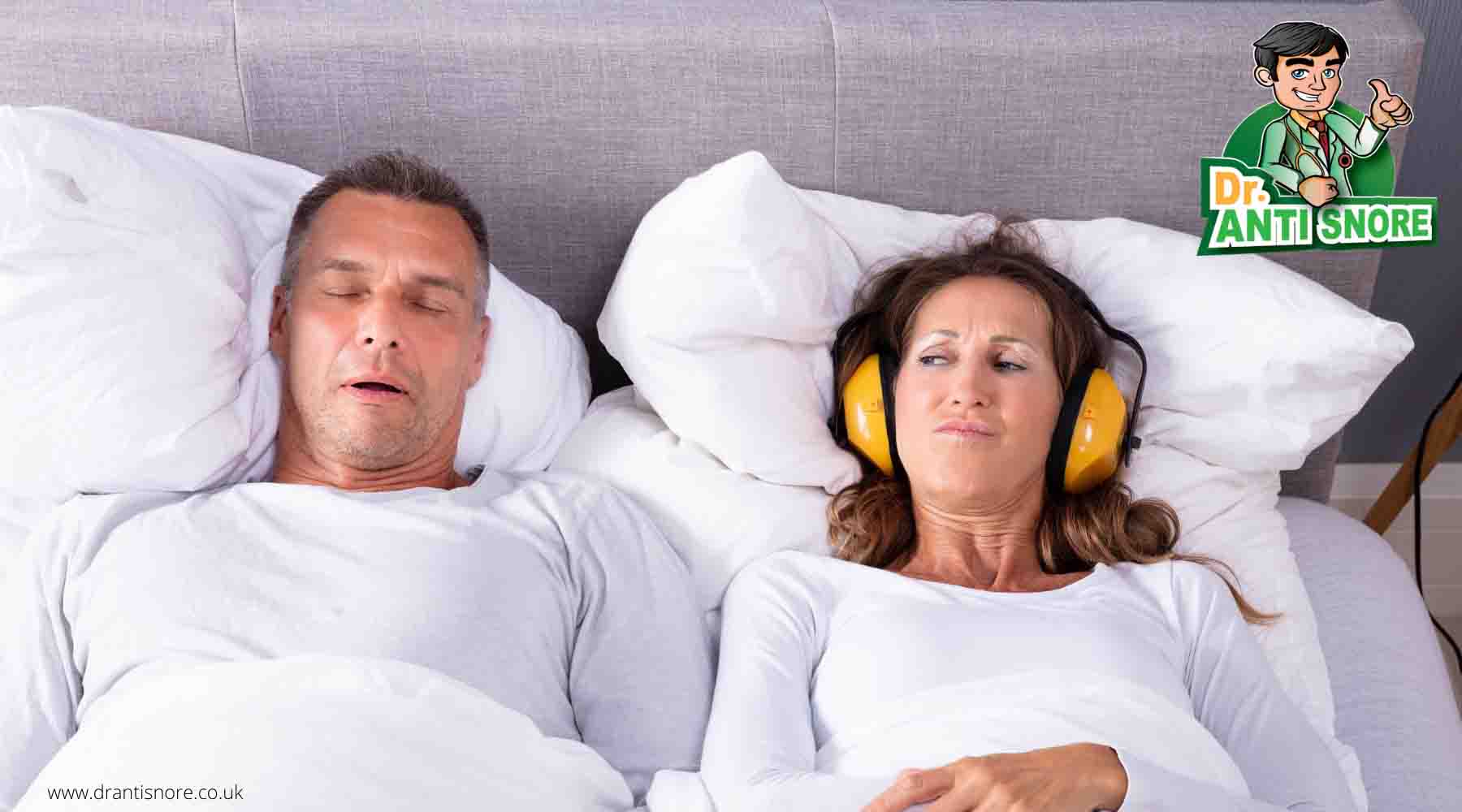

We all find it disturbing whenever a person who sleeps with us produces sharp irritating voices all night. Well, if you also snore, you’re not the single person on Earth. Up to 40 percent of children and 49 percent adults snore.1
Snoring has always been considered as a nuisance and a source of disturbance, but it is actually a disorder with many social and health consequences. If you think that you look hilarious to others while snoring, then rest assured that they also fall into the category of snoring persons.
In this article, you’ll get to know proper explanations on snoring, its causes, types, and available treatment options. So be with the article while we dive into the details!
What is snoring?
Snoring is the hoarse or dissonant sound that is produced while a person is asleep. It is a common sleep disorder commonly occurring in middle-aged persons which predisposes to a serious problem called Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA).
The factors that lead to snoring are obesity, alcohol consumption, drugs intake, hereditary or sedentary lifestyle.2
How does snoring occur?
Snoring happens whenever flowing air is obstructed by any reason during exhalation. This obstruction mostly occurs due to the throat muscles getting relaxed during sleep making the throat narrow. Also, the tongue falls backward in a floppy way. This obstructed air creates increased turbulence and thus vibrates the nearby tissues. Vibration of these tissues leads to the characteristic sound of snoring. Moreover, the narrower your throat becomes, the greater the vibrations and the louder you snore.
Several things that can obscure the airflow are enlisted and highlighted as follows:
- Age: As you age, your throat becomes narrower due to the loss of muscle tone. Although you can’t do anything about you getting older, yet effective lifestyle changes and throat exercises can help prevent snoring.
- Obesity: Whenever a person is obese, excess fat accumulates around the neck. The external pressure by the fat shrinks the air tubes and thus causing increased obstruction to the airflow.
- Nose blockage: People suffer from flu or common cold in winters. Also, most of the individuals are allergic and their nose gets blocked with the mucus or wet booger.
- Deviated nasal septum: Genetic abnormalities cause the abnormal development of nasal septum (the wall separating the two compartments of nose). This deviated nasal septum hinders the movement of air and even sometimes stops airflow completely.
- Alcohol or drug abuse: Muscles of alcoholics get relaxed whenever they drink. It is due to the fact that their brain diminishes its activity and control over the muscles. The relaxed throat muscles obstruct the passage of air. Certain drugs are also able to do so.
- Sleep deprivation: Lack of proper sleep would make you that much tired that your throat muscles would get relaxed while you start sleeping.3
What are the symptoms of snoring?
Let us talk a bit about the symptoms of snoring. Snoring is often associated with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), as already stated above. However, all snorers do not have OSA, but if snoring is followed by the following symptoms, it may be a sign of the worsening of snoring to OSA:
- Not able to sleep in daytime
- Difficulties in concentration
- Uncomfortable sleep
- Sore throat
- Gasping at night
- Pauses in breathing during sleep
- Chest pain at night4
Why does your snore sound different than mine?
There isn’t any kind of complex and intriguing medical concept behind the difference in snoring sounds. Let us get into them a bit and relate them with snoring.
Every sound differs from another because of the major three characteristics: intensity, pitch, and tone. Intensity is the amount of energy a sound has in a given area of space. The pitch helps us to distinguish between low and high sounds. Tone refers to the sound quality or sound pleasantness.5As snoring also produces a characteristic sound, it also possesses specific intensities, pitches, and tones.
Every person snores differently due to the variance in the cause of snoring. Thus, every person produces a sound of different quality with a peculiar intensity, pitch, and tone.
How is the pitch of snore determined?
Due to advancements in science and medical equipment, doctors can now evaluate the acoustic properties of snoring by a technique called sleep nasendoscopy. Results through this procedure have shown that the pitch of snoring sound lies below the frequency of 500 Hz.
The pitch of snoring changes with the vibration of soft palate or other structures involved in snoring.6
Type of Snoring and snoring sounds
Snoring sounds are assessed according to the vibrating tissue e.g., soft palate vibration produces the longest snores of all. Thus, depending upon the location of vibration within the airways, one snore can be very discrete from the other.
- Soft Nasal Snore: When the vibrations occur in the nasopharyngeal tissues because of the obstructed nostrils, the sound produced is quite soft. Nostrils can become obscured by allergies, mucus plugging, or conditions like nasal polyps, etc. Mostly the deviated nasal septum is the underlying cause.
- Louder Oral Snore: Any kind of obstruction within the oropharyngeal passage such as caused by weakened soft palate, enlarged tonsils or deviated uvula, etc. lead to oral snoring in persons who mouth-breathe. Oral snore sound is a bit louder and guttural than the nasal snore.
- Tongue Snore: When the tongue retracts backwards in a floppy way due to its excessive relaxation, it barricades the pharyngeal opening consequently blocking the airflow to the lungs. It becomes difficult for the patient to breathe and the patient thus produces snoring. A study also showed that fatty tongues in obese persons could be the cause of snoring and sleep apnea.7
Snore Map
According to acoustic research of the snore sounds, four possible energy sound types have been measured and a snore map has been designed:
- Type 1: It is a low-frequency single syllable snore.
- Type 2: The snore consists of duplex sounds having both low and middle frequencies.
- Type 3: The snore consists of duplex sounds having both low and high frequencies.
- Type 4: The snore consists of triplex sounds having low, middle, and high frequencies.
Doctors designate a person’s snore a particular type by looking at this snore map.8
Snore Sounds Pattern
The snore sounds are characterized by two patterns, namely:
- Simple Waveform: Vibrations occurring in the open airway lead to simple waveform scores.
- Complex Waveform: Vibrations that occur due to momentary closure of the airway produce complex waveform.9
How can your doctor diagnose the specific cause of your snoring?
Your doctor would ask about your medical history and might also do a physical exam to search out for the problems that could block your airways. In addition to this, he or she might also give you some specific tests such as:
- Sleep study tests: These tests monitor your sleep cycle while you’re asleep at home or spending a night in the lab for the test. This test is called polysomnography that measures the stuff like heart rate, brain activity, and breathing pattern, etc.10
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests include X-ray, CT scan, or MRI scan that are able to locate the blocked structures by producing images.
Are there any clinical treatments to alleviate snoring?
Treatment options for snoring vary from cause to cause. All the clinical treatments currently being used have been explained:
- Non-Surgical Snoring Treatment Options/Anti-Snoring Devices
Most snorers want a comfortable and simple solution to their problem and wearing anti-snoring mouth guards, offer this simple yet effective solution they seek.
Anti-snoring mouth guards are classified as mandibular adjustment devices (MAD) because they adjust the upper and lower mandibles’ positions to allow for non-restrictive airflow in and out of the airway. They also help to contract the airway’s muscles, thus increasing its diameter and ultimately allowing free airflow. SnoRemover™ is a mandibular adjustment device that works with the same principle described above. It is a mouth guard that you have to wear in your mouth before bed. Recent study at the Respiratory Support and Sleep Centre of Papworth Hospital in Cambridge proves that a MAD, like the SnoRemover™, will instantly fix snoring for 91% of its users.
Discover www.antisnoredoc.com for more information.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
In order to keep the airways open during sleep, a machine is placed beside the patient that blows pressurized air into the mask that he or she wears over the nose.
- Invasive Procedures to Correct Anatomic Problems
Several surgeries are also performed to rectify the anatomic problems causing snoring. These surgical options use lasers or radiofrequencies that trim or reshape the abnormal structure such as uvula/soft palate.11
What lifestyle changes can help you stop snoring?
The following solutions and lifestyle changes may surely help you stop snoring:
- Exercising for weight loss: Excessive fat accumulation around the neck is a major cause of snoring. Weight loss is an effective solution for people who are quite disturbed due to snoring.
- Avoidance of alcohol: Alcohol and other sedative drugs reduce the tone of throat muscles, so they must be avoided.
- Usage of specialized anti-snoring pillow: Specialized pillows have been made for the persons who snore. These pillows have a specific height and thickness designed to correctly place the person’s head for preventing snoring.
- Change in the sleep position: Most individuals sleep by lying on their backs. This makes the base of their tongue and soft palate stick to the back of the throat causing blockage. Changing this position to a better position such as on the side may help prevent this.
- Usage of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine: A CPAP machine forcefully pumps pressurized air into your airway overnight, causing any blocked part of airway to remain open while sleeping. This decreases the symptoms of snoring and sleep apnea.12
- Wear a MAD like SnoRemover™: MADs come in various designs and specifications, and these are factors that could affect their effectiveness. SnoRemover™ is made to fit perfectly into your mouth with less or no discomfort at all. It can be custom molded to fit into anyone’s mouth comfortably and micro-adjusted for more or less effect.
Take-Away Message
It is common to feel abashed- not to mention to feel a bit blemish-when your partner complains about your snoring. You probably don’t even intend to snore and this snoring leads to relationship turmoil.
The verdict is clear – you need to get your snoring under control if you want to live with vitality and vigor. It plays a huge role in your wellbeing and the health of your intimate relationships. SnoRemover™ was designed alongside leading physicians as a one-stop solution to kicking snoring habits to the curb for good.
Do you want to wake up more energized, refreshed, and surging with vitality?
Then buy SnoRemover™ at www.antisnoredoc.com and remove this disturbing snoring.
References
1. Snoring – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/snoring.
2. Kaur, S., Baslas, V., Aggarwal, H., Kumar, P. & Chand, P. Snoring: An Annoyance or a Serious Health Problem (Obstructive Sleep Apnea)? Indian Journal of Community Medicine vol. 40 143–144 (2015).
3. Common Causes of Snoring – Sleep Foundation. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/articles/common-causes-snoring.
4. Snoring Causes and Symptoms – Sleep Education. http://sleepeducation.org/essentials-in-sleep/snoring/causes-and-symptoms.
5. The Components of Sound. https://www.nde-ed.org/EducationResources/HighSchool/Sound/components.htm.
6. Pevernagie, D., Aarts, R. M. & De Meyer, M. The acoustics of snoring. Sleep Medicine Reviews vol. 14 131–144 (2010).
7. Fatty tongues could be main driver of sleep apnoea – BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/health-51050566.
8. Lee, L. A. et al. Energy Types of Snoring Sounds in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Preliminary Observation. PLoS One 7, e53481 (2012).
9. Types and Causes of Snoring. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Types-and-Causes-of-Snoring.aspx.
10. Polysomnography: Overview, Parameters Monitored, Staging of Sleep. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1188764-overview.
11. Treatments for Snoring. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/17577-treatments-for-snoring.
12. Snoring Solutions, Aids, & Remedies – Sleep Foundation. https://www.sleepfoundation.org/articles/snoring-and-sleep.