The Art of Quince Tree Pruning: Shaping and Nurturing for Abundance

Pruning, the deliberate cutting and shaping of plants, is an art form as much as it is a science, especially when it comes to the cultivation of quince trees. This comprehensive guide is tailored for enthusiasts and gardeners across Britain, offering step-by-step instructions on how to master the art of quince tree pruning. The objective is not just to enhance the aesthetic appeal of these trees but to ensure a bountiful harvest of quinces, a fruit cherished for its unique flavor and versatility in culinary applications.
Understanding Quince Trees
Before delving into pruning techniques, it’s crucial to understand the basic characteristics of quince trees. Quince trees (Cydonia oblonga) are deciduous, growing to about 4 to 8 meters tall. They are known for their attractive pale pink blossoms, gnarled branches, and large, fragrant, pear-shaped fruits. If you are looking to buy quince trees you should know that they thrive in temperate climates, making Britain an ideal location for cultivating these trees. They prefer well-drained soil and a sunny position, although they are quite adaptable to different soil types and conditions.
The Importance of Pruning
Pruning plays a pivotal role in the health and productivity of quince trees. It helps in removing dead or diseased wood, controlling the tree’s shape and size, and encouraging the growth of strong, healthy branches that can support the weight of the fruit. Moreover, pruning allows for better air circulation and sunlight penetration, which are essential for the ripening of the fruits and prevention of diseases.
When to Prune
The best time to prune quince trees is during the dormant season, from late winter to early spring, before new growth begins. This timing helps prevent the spread of diseases and allows the tree to heal quickly without diverting energy from fruit production. However, dead or diseased branches should be removed immediately, regardless of the season, to maintain the tree’s health.
Tools for Pruning
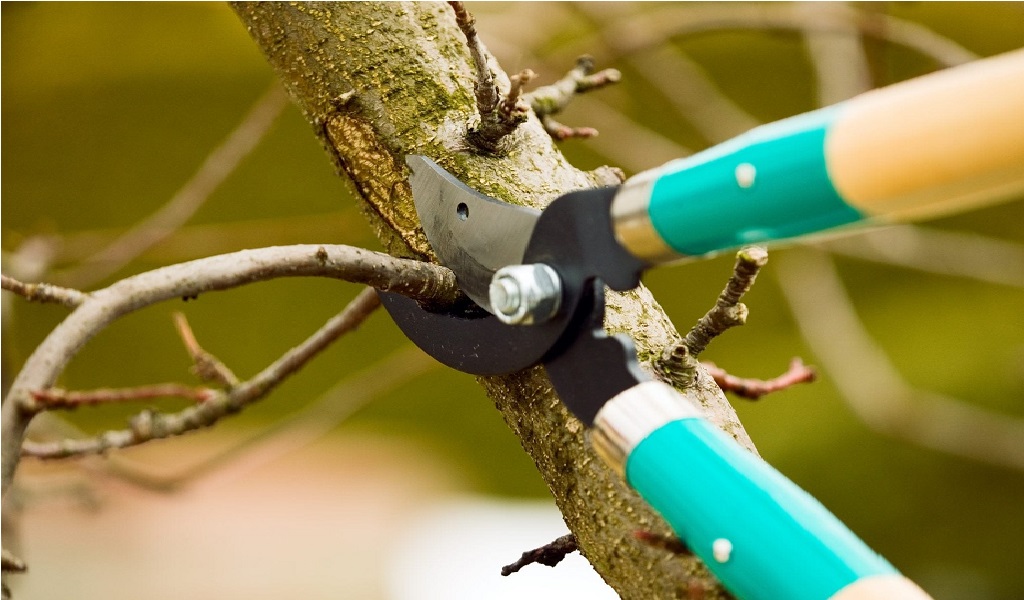
Equipping yourself with the right tools is essential for effective pruning. A sharp, clean pair of secateurs (hand pruners) is ideal for cutting branches up to 2 cm in diameter, while loppers are suited for thicker branches, up to about 4 cm. For larger branches, a pruning saw is necessary. It’s crucial to sterilize your tools before and after use to prevent the spread of diseases.
Pruning Techniques
- Sanitary Pruning: The first step in the pruning process involves removing all dead, diseased, or damaged branches. This is crucial for maintaining the overall health of the tree and should be done as soon as these issues are noticed.
- Structural Pruning: In the early years of a quince tree’s life, focus on shaping the tree. This involves selecting 3 to 5 main branches to form the tree’s framework and removing any competing branches. The goal is to create an open, vase-like shape that allows light and air to penetrate the canopy.
- Maintenance Pruning: As the tree matures, maintenance pruning becomes essential. This involves thinning out overcrowded branches and cutting back branches that are too long or that cross over others, which could lead to damage and disease.
- Renewal Pruning: Older quince trees may require renewal pruning to rejuvenate growth. This involves selectively removing some of the older branches to encourage the development of new, vigorous growth.
Pruning Young Quince Trees
For young quince trees, the focus should be on establishing a strong, balanced framework of branches. Start by selecting a central leader (the main upward-growing branch) and 3 to 5 side branches that are evenly spaced around the trunk. These branches should be at least 50 cm from the ground to allow easy harvesting and maintenance. Remove any shoots or branches that compete with the central leader or that grow inward towards the tree’s center.
Enhancing Fruit Production
Once a quince tree has been structured for optimal growth, the next phase focuses on enhancing fruit production. This involves several key techniques:
- Thinning Out Fruit-Bearing Branches: As quince trees mature, they may produce more fruit than they can support, leading to smaller quinces or even branch damage. Thinning out some of the fruit-bearing branches allows the remaining fruits to develop better in size and quality. It’s a balance between quantity and quality, aiming for a harvest of larger, healthier fruits.
- Heading Back for Vigor: Heading back involves shortening the length of branches by cutting them back to a bud. This stimulates growth lower down on the branch, encouraging the development of new fruiting spurs. This technique is particularly useful for invigorating older trees that have become less productive over time.
- Spur Pruning: Quinces bear fruit on short, stubby branches known as spurs. Over time, these spurs can become crowded or cease to produce fruit. Pruning these spurs—removing old, non-productive ones and thinning out crowded areas—encourages the growth of new, fruitful spurs.
Managing Older Trees
As quince trees age, they require specific pruning strategies to maintain their vigor and productivity. This might involve more aggressive renewal pruning to stimulate the growth of new fruiting wood. For trees that have been neglected or have become overgrown, a more drastic approach may be necessary, sometimes removing up to one-third of the tree’s branches. This should be done cautiously over several seasons to avoid shocking the tree.
Water Sprouts and Suckers
Water sprouts (vertical shoots that grow from the trunk or branches) and suckers (growth from the base of the tree or roots) can sap energy from the rest of the quince tree, diverting resources away from fruit production. Regular removal of these is crucial. They should be cut back to their point of origin to maintain the tree’s energy focus on producing high-quality fruit.
Seasonal Care and Monitoring
Beyond the act of pruning, the art of nurturing quince trees to abundance involves ongoing care and vigilance. Seasonal care, including mulching, watering, and feeding, supports the health of the tree and its capacity for fruit production. Monitoring for pests and diseases and taking prompt action at the first signs of trouble ensures that your quince trees remain robust and productive.
Final Thoughts
The art of quince tree pruning requires an understanding of the tree’s growth patterns and needs over the years. Mastering these techniques promises not just the joy of nurturing these beautiful trees but the reward of bountiful harvests of quince.